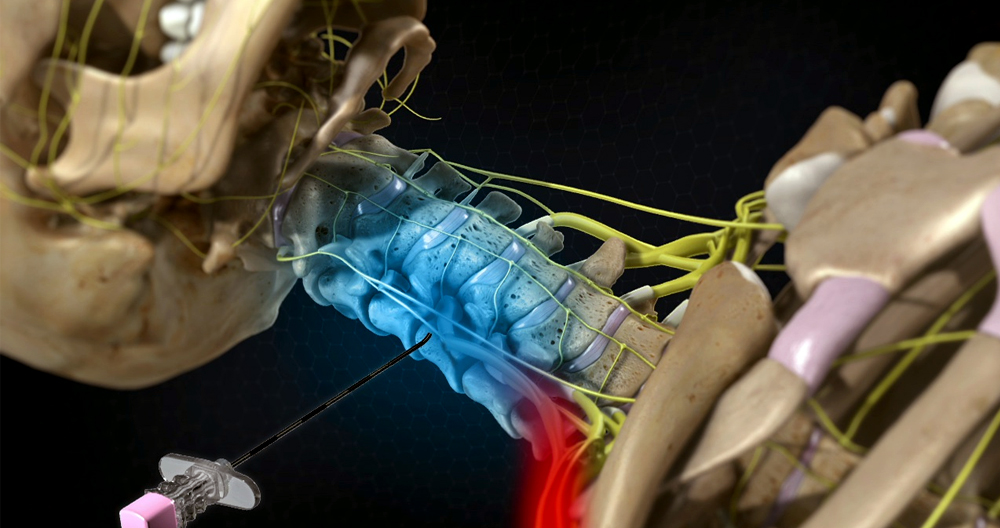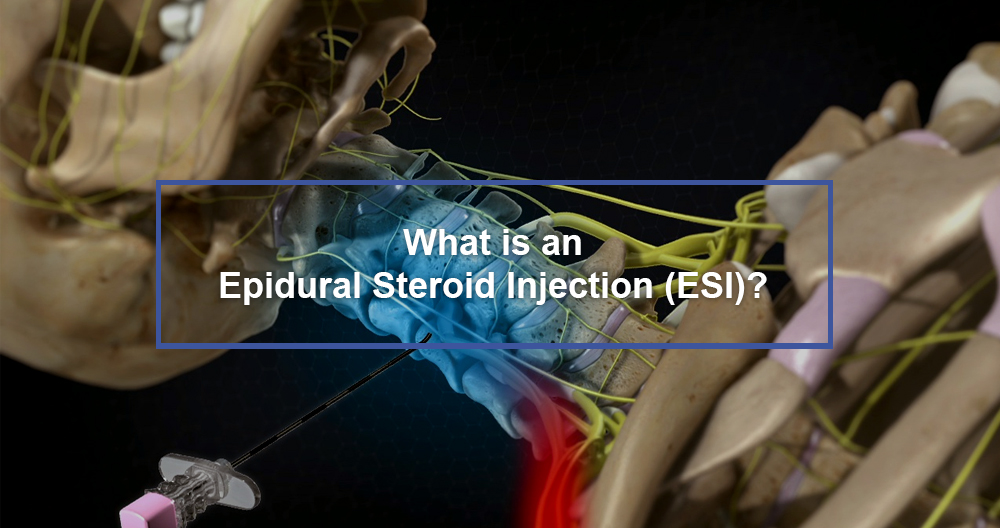
An injection with steroids is a combination of a corticosteroid (such as triamcinolone/methyl-prednisolone), and an anesthetic (such as lidocaine) or buprevaine. The drugs are injected in the epidural zone of the spine. This is the area between bony vertebrae.
Corticosteroid injections are very effective for relieving inflammation. They can also be administered directly at the pain area. The injection will not shrink the herniated disc. It only affects the spinal nerves by removing the swelling proteins. It can provide pain relief that lasts for many days or even several years.
Who are the potential candidates?
ESI could be beneficial for patients with neck or arm pain (sciatica), leg pain (sciatica), and low back pain (sciatica). These conditions are well-suited for ESI.
- Spinal stenosis, or narrowing of the spinal canal and nerve root channel, can cause leg and back problems.
- Spondylolisthesis describes a weakness of fracture that occurs between the top and bottom facets of a vertebra. The vertebra can move forward and compress the nerve roots.
- Herniated disc: When the gel-like substance contained within the disc ruptures or bursts through the weaker region of the surrounding wall (annulus), it is called a herniated dis. This substance can cause irritation, pain, swelling, or nerve damage if it comes in direct contact with the spinal canal.
- Degenerative disc: This is when the intervertebral space between the disc (and the annulus) collapses, tears the annulus, or causes the growth and development of bone spurs.
- Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that runs along the sciatic, buttocks, and down to the legs. It’s often caused by compression or the 5th or 1st of the lumbar spine nerves.
Many patients have found ESI beneficial in the management and prevention of painful inflammatory diseases. ESI is a tool that can help you determine if you need to have surgery for pain due to a herniated disc. The use of epidurals is to ease pain that interrupts rehabilitation.
Patients with bleeding disorders or infections should not have ESI. A slight rise in blood sugar may be experienced by patients with diabetes. Patients with glaucoma could experience a temporary rise in blood pressure. Discuss this with your doctor. If you believe you may be pregnant, tell your doctor. Fluoroscopy x-rays could be dangerous for the baby.
Who is responsible for performing the procedure?
A variety of doctors can administer epidural steroid shots, including radiologists, surgeons as well as physiatrists.
What happens before treatment begins?
The doctor will review your medical history, as well as any imaging studies, to determine which needles are best injected. During your appointment, you’re welcome to ask any questions. Plavix and Coumadin are blood thinners. Patients may need to stop using them. Your ESI may require you to stop taking the medication a few days before. Talk to your doctor about all medications and the doctor who will administer injections. The procedure is performed using xray fluoroscopy in an outpatient center. It’s possible to arrange for someone to drive your vehicle to the center on day of the injection.
What happens during treatment
You will need consent forms signed and to list any medications you are taking. The process can take up to 45 minutes. The recovery period will begin after that. It is essential to deliver the medication as close and as quickly as possible to the nerve. The type and extent of your medical history will impact the choice of injection. The doctor will help you choose the right type of injection to achieve the best results.
Step 1 – Prepare the patient
The patient lies flat on an x-ray table. The local anesthetic provides pain relief. The patient must be alert and awake during injections to provide feedback to the doctor. Based on the center’s recommendation, Versed or Valium can be prescribed.
Step 2 – Insert the needle
To guide the hollow needle through the skin between bony spines and into epidural space, the doctor uses x-ray fluoroscopy. Fluoroscopy enables doctors to monitor the needle via an x-ray monitor and ensure that it is in the right place. Some discomfort is normal, but patients will feel less pain than pressure.
There are many types of ESIs.
- Cervical ESI, neck. The needle entry point for the neural foramen is located on the neck. It is located just above where the nerve root opens. A contrast dye can be used to confirm that the medication is located.
- Lumbar ESI is located lower back. The needle entry point is located slightly above your midline. Contrast dyes are used to confirm that the medication is in the correct location.
- Caudal ESI (tailbone). To reach the lower spinal nerves, the needle should be inserted into sacral hiatus (just above the tailbone). A contrast dye can be used to confirm the flow of medication.
Step 3 – Inject the medication
Once the needle is properly placed, the medication and corticosteroid medication will be injected into an epidural space that surrounds the nerve roots. The needle is then pulled out. Depending on the pain location, the procedure can be done on either the right or justify side. You can inject one or more spinal levels.
What happens next?
Most patients can walk right away after the procedure. After a brief stay, most patients can leave the center. If you experience temporary weakness or numbness of your legs, you will need someone to accompany and drive you home.
Patients can resume normal activities the day after. Tylenol, Ice, and Tylenol can help reduce swelling around the injection site. It might be worthwhile to keep track of your pain levels for the next few weeks. As the numbing medicine wears off, you may feel an increase or decrease in your pain. Patients should follow up with their physician following the procedure. This will enable them to verify the effectiveness and discuss any future plans.
What were your results?
Many people find ESI pain relief [1,2]. Two to three additional injections may be necessary if mild pain relief is desired. These injections are typically given every 1-4 week. This will ensure you get the full benefit. There are many factors that can affect the duration of pain relief. They may last for weeks, or even years. For future pain episodes prevention, you can combine injections with physical therapy or home exercise programs.
What are the possible dangers?
ESI presents few risks and can be recommended for certain patients. Injecting the needle poses very rare risks. These risks include spinal headaches, bleeding, infection, and puncture wounds. Also, nerve damage/paralysis can occur (rarely).
Side effects include weight gain and flushing (hot flashes), flushing. The mild numbness in the affected arm or leg will usually go away in less than 8 hours. This is similar to facial numbness after dental work. Patients with chronic conditions such heart disease, diabetes, or even rheumatoid arthritis should consult their doctor.
What are epidural injections of steroids?
An epidural injection of corticosteroid medication places medication directly around pinched neurals that exit the spine in an epidural space. The epidural spaces are located between the spinal cord and nerves as well as between the discs of the spine and bones. This is the area where disc tissue can protrude into the spinal canal and cause pressure on or inflammation around nerves.
What is the purpose and function of epidural corticosteroid injectables?
The most common use for epidural steroids in back pain is to treat sciatica, lumbar radiationopathy, spine stenosis or herniated disc. The powerful anti-inflammatory medication corticosteroids can also be injected into the epidural cavity to reduce inflammation and pain around an irritated neural that causes back or leg pain.
Who would benefit most from an epidural shot of steroids
Patients suffering from common conditions such a lumbar disc or a lumbar nerve injury may find an epidural injectable helpful. Degenerative disc disease and herniation of sciatica. An epidural injection may be an alternative treatment to surgery.
How do epidural corticosteroid injectables work?
The injections of epidural steroids provide a powerful anti-inflammatory for nerve impingement locations in the spine. They may contain saline, local painkillers, or steroids. The individual may have a different volume and concentration.
There are three possible routes for administering epidural injections to lumbosacral’s spinal cord.
- caudal
- Interlaminar (also translaminar).
- Transforaminal
Your physician will help you decide the best treatment based upon your condition and previous spine surgery.
- The caudal injectable is the most direct way to access the epidural areas. However, it can also be the most precise. This is useful if several parts of the spine need to be accessed or if alternative options are not feasible.
- Injections that are either translaminar (interlaminar) or translaminar deliver the medication directly into the epidural spaces at affected levels. They can be targeted on one side or both, and can treat multiple levels at the same time.
- Transforaminal injections deliver medications to the nerve root. This is done by compressing and rupturing the disc. This is the first step for epidural injectables.
How often can epidural steroids be administered?
It is recommended to give epidural steroid injections up to three to six occasions per year. The injections can be administered at intervals of several weeks if the disc herniation was not previously experienced. This will provide immediate and complete relief. It is not unusual for chronic diseases to go more than three to six years between injections.
How long can epidurals for back pain last before they stop working?
Patients with disc herniations may feel permanent relief if they are responsive. Patients with chronic pain and recurrent dislocations should expect to experience relief within three to six weeks.
What are the potential dangers associated with epidural injections of steroids?
All procedures that involve a needle have risks. There is the possibility of infection, bleeding and nerve damage. The potential risks are often minimal when the procedure is done correctly.
There are some contraindications for epidural steroids injections.
- Anticoagulation/bleeding disorders
- medication allergies (rare)
- Systemic infection or localized infected areas
What side effects may epidural steroids injections produce?
Common side effects include slight discomfort at the injection site, temporary worsening or normal pain, flushing and insomnia, as well increased blood sugar. These side effects typically disappear within one to three hours. A less common side effect is headache.
How do I prepare? Is it necessary to eat before or during an epidural steroid injection
Your doctor will give specific instructions. These will depend on which facility you have and what type of epidural you are using (lumbar or cervical, thoracic, cervical). It is common to perform the procedure under local anesthesia.
What is the purpose of anesthesia and how does it work? Is epidural steroid injection painful?
The epidural is then inserted. A local anesthetic will be applied to the skin. The procedure isn’t painful but can cause mild discomfort.
Are I required to lie down on my stomach after and during the procedure?
The procedure takes between 10-20 min. If they have fluoroscopy (X-Ray guidance), patients will need to lie on their backs. After a brief monitoring period you will be able to stand again as normal.
Who administers epidural steroids?
HSS epidural-steroid injections are possible by a variety of doctors, including pain managers, interventional radiologists, physiatrists, and others. All these doctors can safely perform the procedure.
Potential benefits from epidural steroid injections
An epidural is a good option if you have severe back or leg pain. However, epidural injections may not be as effective as they should and pain relief can take up to one year.
You might need to inject up to three times per year, if your first is successful.
You can get the following benefits from steroid injections in the lumbar epidural.
- You can reduce nerve pain and inflammation. Steroids can reduce nerve pain, inflammation, and swelling.
- Limit oral medication. These injections may be used to reduce the need for oral medications. Some of these side effects can occur if you take them long-term.
- Continue to engage in physical therapy or re-engage. Continue or re engage with physical therapy.
- Postpone surgery. Postpone surgery.
There are many methods available for administering epidural injections. It all depends on the patient’s health and needs.
Epidural Injection Approaches
This injection delivers a powerful anti-inflammatory medication directly to your pain area. It can provide pain relief that is immediate and substantial. One option is to use an epidural injection.
- Transforaminal route – This technique allows for the precise administration to the epidural, where it is most likely to be inflamed. This technique injects specific nerve roots to decrease inflammation and pain.
- Interlaminar Route : The needle can be inserted at the backside of your spine. The medication will then be deposited in the epidural. This method is more precise since it does not deposit medication near to the target nerve root. The epidural area is safe from the spread of the steroid solution.
- Caudal route. This is a simple way to treat your pain. Medication is not directed to the epidural or around the nervous system. Although not as effective, the caudal approach may be safer and easier. This can be an effective option for managing diffuse or widespread pain.
The doctor’s knowledge, skills and diagnosis will decide the path of administration.
Effectiveness of injections
Research shows that these injections produce generally positive results. It is possible to give up to three injections in 12 months.
Although epidural injections of steroid steroids have been proven to be effective for pain relief in the short-term, their long-term effectiveness is not clear. They are still controversial in terms of their effectiveness in pain relief and function improvement.
There are limitations to research as well.
- While fluoroscopic guidance can sometimes be used in some cases, not every study includes fluoroscopy.
- Other studies don’t assign patients based on their diagnosis. They tend to lump various types of pain together.
These methodological weaknesses could limit the utility or usefulness of the research. More research is needed to fully understand epidural steroid’s role in sciatica pain and lower back discomfort.
Epidural Steroid injections
Lumbar Epidural Injections is a common treatment for lower back pain.
- Lumbar Herniated disc.
- Lumbar Degenerative disc disease
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
These injections are also used to treat back pain ( Axial Back pain ) and neurogenic Claudication (back or leg pain while walking) less often.
Who Injects?
This type injection is done by spine and back pain management specialists like anesthesiologists and radiologists as well as spine surgeons and spine surgeons. This procedure can be performed at a hospital.
Potential risks and contraindications associated with epidural injectables
The epidural steroid injections may be considered safe and minimally invasive. Some patients may experience temporary side effect, including but not restricted to:
- Post-injection pain
- Nausea
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Fainting (vasovagal assault).
- Flushing the Face
These side effects are usually gone within minutes or hours. These side effects generally resolve within a few hours to hours.
Lower risk at L4 and lower spine levels
An epidural for spinal levels lower than L4 has a lower likelihood of complications. Fluoroscopy helps guide the needle to avoid nerve and artery damage.