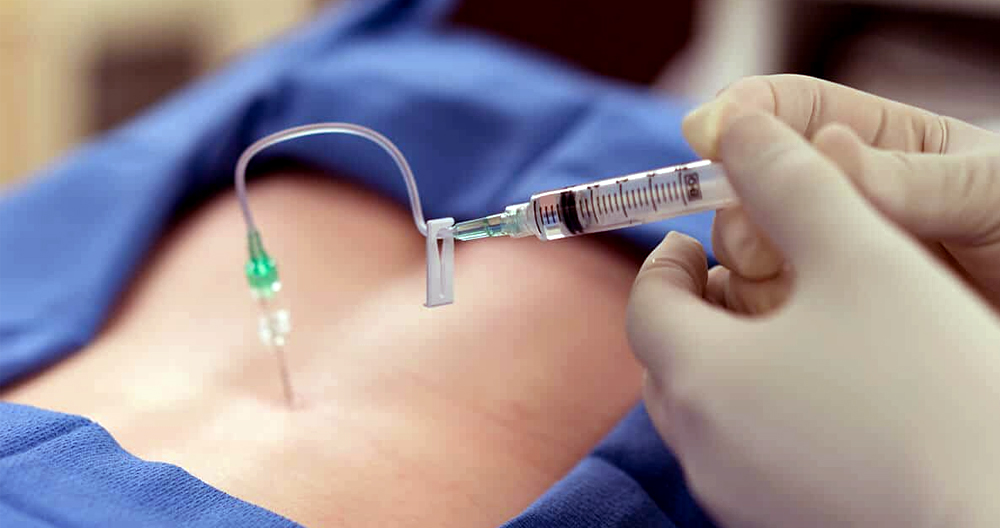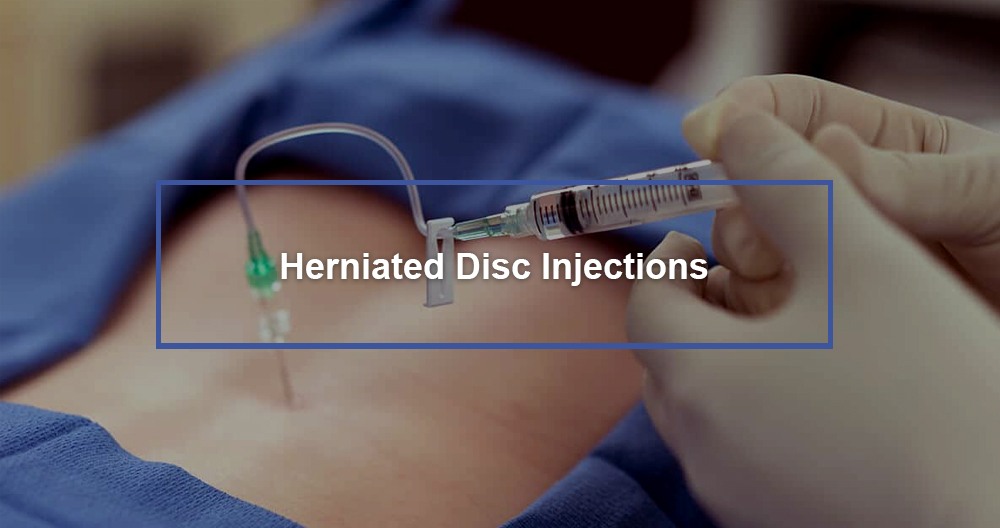
An epidural corticosteroid or steroid injection, which is simply a way to inject pain medicine quickly into your body using a needle, is the simplest explanation. The medicine is injected into an epidural area. This is a densely fatty area that covers the spinal cord to protect it and its surrounding nerves. Sometimes pain relief lasts only a few days. Sometimes the benefits last for a while.
Back pain is a common problem. Around 2% of adults will experience it at some time. A herniated or slipped disc is also known as a ruptured or slipped disc. This happens when a small fragment of the disc pushes into the spinal canal, increasing pressure on nerves. The pain can be severe, debilitating, or even fatal and last for varying lengths of times. The doctor may recommend epidural steroid injections if you are experiencing persistent herniated disk pain.
What is a Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection?
A lumbar epidural medication injection (lumbar-ESI) is an injection containing anti-inflammatory medicine. This medicine can be either a corticosteroid or steroid. It is administered to the epidural area around your spinal nerves. The purpose of lumbar epidural injections of steroids is to manage chronic pain that results from irritation and inflammation of your spinal nerve roots in the low back (the area at the lumbar of your spine). Lumbar Radiculopathy (radicular pain) refers to chronic low-back pain. It can radiate down to your hips or legs, and/or your feet.
What is an epidural steroid injection for?
A quick epidural injection can provide relief for severe pain in the arms and legs that is difficult to treat. The nerve passages connecting your spine and arms to your legs or arms can become narrowed. This can cause severe pain. This can lead to inflammation of the spinal nerves.
There are a number of factors that could contribute to this narrowing.
- Herniated disks
- “Slipped” vertebrae
- Joint cysts
- Bone spurs
- Due to spinal arthritis, thinning of ligaments in the spine
Injected steroids decrease inflammation and open these passages to provide pain relief.
How does a lumbar epidural steroids injection work?
Chronic pain management may be recommended by healthcare providers. Your provider will inject a steroid, or corticosteroid medication, into the epidural area by your spinal cord at your low back.
The lumbar spine is located in the lower back of your spine. This area comprises five vertebrae. They are the largest vertebrae within your spine. They reach from your lower chest (chest), to your sacrum (the base of your spine).
Your spine is composed of 33 interlocking, individual bones known as vertebrae. They run from your brain’s base to your tailbone. These bones provide protection for your spinal cord, and allow you to twist and turn. These disks are located between your vertebral bones and provide flexibility for you as well as cushioning for the vertebrae.
From top to base, you will find five vertebrae within your lumbar spine. They are called lumbar 1 through lumbar 5. There are several roles that the lumbar vertebrae perform, including:
- Your upper body is supported and stabilized.
- Allowing twisting, bending and other movements
- Protecting your spine cord and cauda-equina (the spinal nerves that descend from your bottom)
- Your spinal cord, a bundle of nerves running from your brain down to your lower back, is very important. Your spine acts as a highway linking the nerves throughout your body and your brain. This allows your brain to communicate with the rest.
Sometimes, nerve roots that attach to the low back (lumbar) region of your spine cord can become pinched. This could happen, for instance, if you have herniated discs. The pain can radiate down your legs from inflamed or inflamed nervous systems.
A lumbar epidural injection of steroid is when your provider injects a drug into the epidural area around your spinal chord. Your spinal cord is enclosed in the epidural space like a sleeve. It contains fat and connective tissues. The steroid is used to reduce swelling and pressure on nerves. Lumbar epidural injections of steroid steroids usually provide temporary pain relief for up to three months. But, some people may experience no or less pain relief after the injection.
What are lumbar epidural injections for?
To manage chronic pain caused by irritation or inflammation of the spinal nerve roots, healthcare professionals use lumbar epidural injections. Lumbar radicular or sciatica pain is sometimes called sciatica. Lumbar Radicular Pain can lead to the following symptoms:
- Pain.
- Numbness.
- Muscle weakness
- Tingling.
You may experience lumbar radioculopathy (sciatica) from irritated spinal nerve roots.
- Lumbar herniated disk: Also called a slipped disk, ruptured or bulging disc. Soft, gel-like disks have an outer layer that is firmer and has a soft center. The outer layer of disks can crack due to injury or wear over time. When the inner substance pushes against a crack in the disk between your low back vertebrae, it is called a lumbar herniated. The leaked material can press on the spinal nerves and irritate them.
- Lumbar degenerative disk syndrome: This happens when the padding between your lower back and the vertebrae starts to wear down. Your spinal nerve roots could become inflamed if a degenerated disc is present.
- Lumbar spinal stenosis (lumbar spinal narrowing): This condition refers to the narrowing or narrowing of one or more spaces in your spine. The amount of space your spine has is smaller, which makes it less accessible for spinal nerve roots. The nerves can become pinched or irritated if there is not enough space. This can cause low back pain.
- Lumbar osteoarthritis (lumbar Spondylosis), also known as low back osteoarthritis, can be caused by wear and tear of aging. Lumbar osteoarthritis (lumbar spondylosis) can cause narrowing in your spine or at the points where the spinal nerves exit from your low back. This can cause inflammation and irritation.
The following conditions can be treated by lumbar ESIs:
- Axial low back pain (or localized low back pain): The causes of axial low back pain are many and can be varied. The pain can be sharp or dull and can occur frequently or infrequently.
- Neurogenic claudication occurs when the spinal nerves of your lumbar spine are compressed. It can cause pain and tingling in your lower back, your hips, legs and buttocks. These symptoms are more common when you stand straight or walk.
How common is lumbar epidural pain management steroid injections?
Radicular pain management is one of the most popular types of treatment.
The fifth most common reason Americans seek medical treatment for back pain is due to leg pain. In fact, approximately 9% to 25% describe low back pain (radicular pain) as their number one complaint.
Who does a lumbar epidural injection of steroids?
Lumbar epidural injections of steroid steroids are extremely precise. Therefore, healthcare professionals who administer the injections must have significant specialized training. These healthcare professionals may be qualified to administer lumbar ESIs.
- Physiatrists (Physical Medicine, Rehabilitation providers).
- Radiologists.
- Anesthesiologists.
- Neurologists.
- Surgeons.
How do I prepare to receive a lumbar epidural injection of steroid steroids?
Your healthcare provider should know if you are pregnant or may become pregnant during your lumbar ESI. It is also important to inform your provider about any medications that you take, including herbal supplements and other non-prescription drugs.
Your healthcare provider can give you detailed instructions about how to prepare for your ESI injectable. You should follow the instructions. Your provider may:
- Prior to your lumbar ESI, you should limit eating or drinking.
- Take care of any blood thinner medications and adjust your medications.
- For the best diagnosis, have your back scanned by MRI or CT before you go to your lumbar ESI.
- If you plan to take a sedative in your lumbar ESIS, ensure you have someone to drive you home.
Some questions you might ask your healthcare provider before getting a lumbar epidural steroids injection are:
- How often are you performing lumbar EISs?
- What can I do to prepare for my lumbar ESI preparation?
- What are the possible risks of a lumbar ESI and what can you do about it?
- How will my lumbar ESI feeling be?
- What is the life expectancy of my lumbar ESI?
- What are my other options if a lumbar ESI does not relieve my pain?
- What happens during a lumbar epidural steroids injection procedure?
Most likely, your lumbar epidural will be administered in a hospital or outpatient clinic. The average lumbar ESI procedure takes 15-30 minutes. This procedure is best done while you are still.
There are many ways that your healthcare provider can reach the epidural space surrounding your spinal cord and low back.
- Interlaminar ESI(IESI): The needle’s path is located between two laminae on your spine. This allows you to reach the epidural space. A lamina refers to the flat plate made of bone and that forms part of each vertebra of your spine. The spinal cord is protected and protected by the laminae. Providers often use interlaminarlumbar ESIs for temporary pain relief from disk herniation, spine stenosis and localized (axial or radicular) low back pain.
- Transforaminal ESI, (TFESI): The needle’s path is through the foramina. This is the area through which your nerve roots exit your spine. To temporarily treat radicular pain from disk herniation or an injury to one nerve root, providers commonly use transforaminal Lumbar ESIs.
- Caudal ESI (Cause-specific injection): To reach the lowest spinal cords, the needle will pass through the sacral Hiatus. This is located at the bottom of your sacrum just above your tailbone. Your sacrum is the triangular, low-back bone between your hip bones. For temporary pain relief, providers might use a caudallumbar ESIS to treat “failed back”. Compared to interlaminar and transforaminal ESIs, the risks of caudal ESIs are generally lower.
A lumbar epidural steroid injectable procedure involves the following steps:
- After you have changed into a medical dress, you will lie on your belly on a flat table. A pillow will be placed under your abdomen. Your healthcare provider might give you medication to relax such as a sedative.
- Your provider will carefully clean the area where the epidural is to be inserted. This will minimize the chance of infection.
- To guide the epidural needle in the right place, your provider will use fluoroscopy (Xray or radiology imaging).
- A small needle may be used to inject local anesthesia near the epidural site. This is to ensure you don’t feel any pain during the procedure.
- The provider will inject a contrast substance once the epidural catheter is in place around your spinal cord. The contrast material will ensure the needle tip stays in the epidural area and not inside any other tissues or blood vessels. This makes it easier for the medication to reach the targeted nerves.
- Your provider will then gradually inject the medication. It is typically an anti-inflammatory medication like a steroid, corticosteroid, or steroid. Some providers may inject a combination of corticosteroid and normal saline.
- Once your provider is finished with the injection, they will apply pressure on the area to stop bleeding. They’ll also clean the area and apply a dressing. The provider will place you in a chair, or on a bed, to rest for between 30 and 60 minutes. This is so your provider can ensure you have no reactions to the medication before going home.
How painful can a lumbar epidural steroids injection be?
It is possible to feel a small pinch in your back when your provider injects local anesthetic. This will numb the area prior to your lumbar epidural.
You might not feel any sensations during your lumbar electrostimulation (ESI), or you may feel these:
- Pressure.
- Tingling.
- A burning sensation.
- Momentary pain
If you feel any discomfort, it will usually go away after the injection is complete. Your provider should be notified immediately if you experience intense or sharp pain during or following your lumbar ESI.
What side effects are there from lumbar epidural injections of steroid steroids?
Side effects of lumbar electroshock inducing drugs include:
- The steroid medication may cause temporary discomfort.
- It is possible to feel tenderness, swelling, or bruising near the injection site.
- Your provider may use fluoroscopy to provide imaging guidance. There will be very little radiation exposure from the X-rays if this is the case. Fluoroscopy Xrays could be harmful for unborn babies. Before having the procedure, it is important to inform your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or may become pregnant.
- An epidural injection of steroids will most likely result in high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) for those with diabetes. This could be for hours or days.
- Glaucoma patients may experience temporary increases in blood pressure and/or eye pressure with an ESI.
How long does a lumbar epidural steroids injection take?
The pain you feel may get worse after your lumbar electrostimulation. It will take two to three days for it to start improving. Pain relief can last from a few days to several months.
BENEFITS / RISKS
What are the advantages of lumbar epidural injections with steroid steroids? These are some of the benefits of lumbar epidural injections with steroid steroids:
- Some people may feel temporary relief from pain.
- It is possible that you have enough pain relief to be able to participate in rehabilitation exercises for low back pain.
- Through pain relief, you may enjoy a higher quality life and better ability to carry out daily activities.
- Lumbar epidural injections of steroids may be able to reduce the need for more invasive procedures like surgery, in order to manage pain.
What are the potential risks and complications of injections of steroid lumbar epidural?
While epidural steroid injections for the lumbar region are safe and effective, there are still risks associated with side effects or complications. Although complications and side effects are uncommon, there are risks associated with lumbar ESI.
- Low blood pressure can lead to lightheadedness.
- Grave headaches due to spinal fluid leakage
- Infection after an epidural procedure such as an epidural infection, discitis and osteomyelitis.
- Negative reactions to medication, such as hot flashes and rash.
- Bleeding occurs when a blood vessel is inadvertently damaged during injection. This can cause a hemorhage or blood clot.
- There was nerve damage at the injection site.
- Temporarily lose control of your bladder, bowels and bladder. A catheter, a small tube that fits inside your bladder, may be necessary to assist you in peeing.
- Too many ESI injections, or taking higher doses of steroid medication, can cause damage to your spine and nearby muscles. This is why most healthcare providers limit patients to only two to three ESIs per calendar year.
Is there a long-term risk of side effects from lumbar epidural injections?
Even though it’s rare, long-term complications can result from lumbar epidural injections of steroid steroids.
- Permanent neurologic deficit as a result of spinal cord or nerve root injury from epidural inject.
- Chronic pain from epidural injections to the spinal cord and nerve roots.
- Permanent paralysis caused by a hemostasis, which occurs when blood builds up between the dura mater and your spinal chord.
What is the outlook for lumbar epidural injection therapy?
People often experience temporary pain relief with lumbar epidural injections. Some even experience lasting relief for up to 12 months. Some people experience no pain relief from ESIs. Lumbar epidural injections of steroid steroids are designed to provide temporary pain relief. You can either start or continue physical therapy, or you can avoid more severe pain relief. Long-term pain relief may be possible through physical therapy, which strengthens the muscles supporting your spine. If a lumbar ESI results in pain relief and works well, your healthcare provider may recommend a second injection. The majority of providers limit you to two to three ESIs a year.
What happens after epidural corticosteroid injection procedure?
You can go home once the procedure has been completed. Most people can return to their normal activities within a few days. The steroids work in a matter of days. You might take up to one week to experience the benefits. Injections can be used to improve pain and function for several months. It is possible to repeat the procedure if the injections are effective. If you experience any side effects, please contact your healthcare provider immediately. Talk to your healthcare provider about pain relief if you don’t feel it. This could indicate that the pain is coming in from somewhere other than the spinal cords.
When should I visit my healthcare provider?
After your lumbar ESI has ended, if you feel any of the following symptoms, you should immediately contact your healthcare provider.
- You may feel a severe headache when you stand up, or if you sit down. This could be due to a dural puncture.
- A fever is a sign that you have an infection.
- A loss of bladder control or bowel control, whether it is complete or reduced.
- A nerve injury could cause weakness or numbness in your legs.
Next steps
Before you agree to the procedure or test, ensure you are aware of the following:
- The name of the procedure or test
- Reason you are having the test/procedure
- What you can expect and what they should mean
- The risks and benefits of the procedure/test
- What are the possible side effects?
- When and where will you have the test/procedure?
- Who will conduct the procedure or test and what are their qualifications?
- What would happen if the test or procedure was not performed?
- There are other options or procedures that you could consider.
- What time and how do you expect to see the results?
- For questions or concerns, call the person who performed the test.
- How much will it cost to have the procedure or test done?