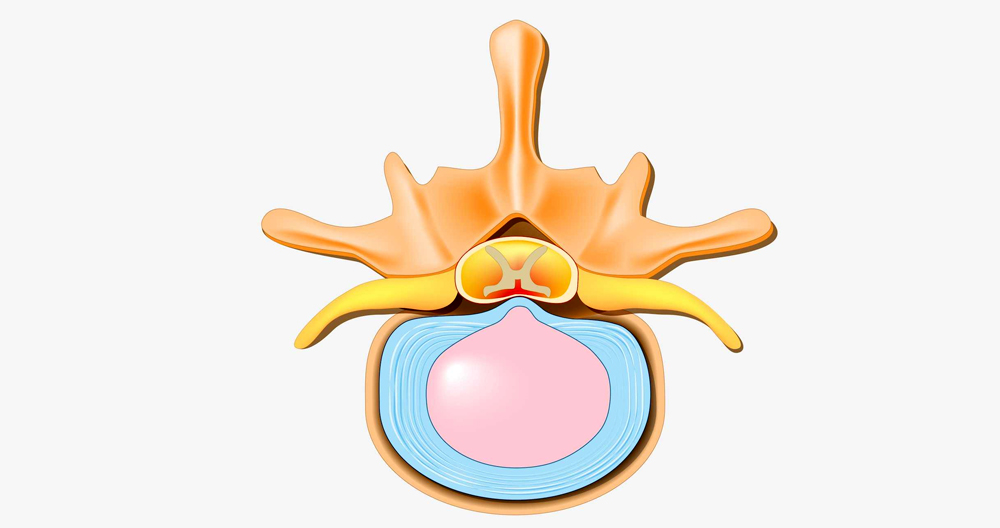
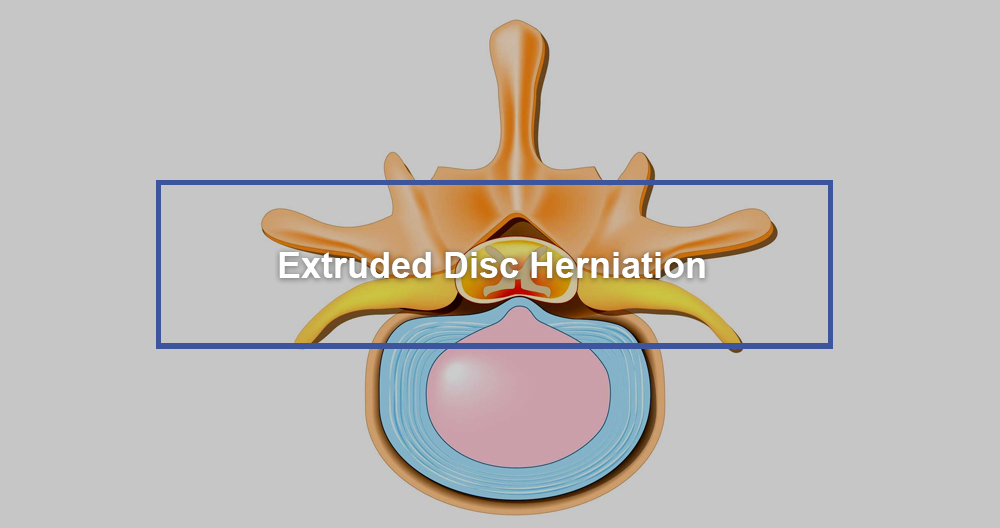
What is an extruded Disc Herniation?
Extruded is sometimes referred to as a herniated (or ruptured) disc. An extruded (or herniated) disc is a condition when the intervertebral distal disc becomes weaker and bulges into the spine canal. These extruded discs do not cause symptoms. Sometimes, an extruded spline disc can compress the spinal cord or cause pain to existing nerves. You might feel pins and bumps, weakness, tingling, or tingling at nerve sites, as well pain in the affected extremity.
There are several ways disc extrusion herniation could occur. An unhealthy lifestyle can increase your risk of developing extrusion disc herniation. More pressure is placed on the spine by poor eating habits and excessive weight. The intervertebral discs that cushion the spine with their spongy content, decrease in effectiveness with age. Over time, discs become fragile and weaker. The discs can become brittle and weak over time. This could lead to tears within their outer wall, which then allows them to herniate. Because discs can freely move in these areas, they are more likely than others to herniate.
3 TYPES HERNIATED DISCS
There are three types. These are classified by the condition of either the nucleus pulposus or annulus fibrosus.
- Disc protrusion. The disc’s jellylike outer core bulges, but the fibrous outer layer is unaffected.
- Disc extrusion. The inner core material, which looks jelly-like and breaks down the fibrous outer, escapes into the spine channel. The inner core material of the disc remains attached. This type can be referred to as a “disc protrusion” or “disc extrusion”.
- Disc sequestration. The jelly-like inner layers break through the fibrous outer layer and separate the disc. It may be found floating around the spinal channel or in one of the passageways leading from it. This type could start as a disc protrusion and progress to disc isolation.
Disc herniations can lead to pain, inflammation and other symptoms. Symptoms can worsen if disc injury is more severe.
While disc herniation is possible anywhere on the spine. However, it’s most common in the cervical spine. Low back and neck area are the most mobile.
HERNIATED DISCS SYMPTOMS
In some cases, disc protrusion may not cause pain and symptoms. There may be symptoms if the jellylike disc nucleus is leaking. If you’re experiencing symptoms, the following could happen:
Cervical spine
- Neck pain
- The pain radiates down towards the armpit and shoulders.
- Numbness, weakness and tingling radiating down arms and fingers
- Neck spasms
Lumbar spine
- Low back pain
- Sciatic pain can refer to pain radiating down your buttocks, thigh or legs.
- A feeling of tingling or weakness that radiates down the legs, feet and ankles
- Back spasms
Symptoms often only appear on one side.
HERNIATED DISCS TREATMENTS OPTIONS
To see if your disc is herniated, your doctor will order an imaging scan, such a MRI. This will enable your doctor to assess the extent and nature of the herniation. Extruded spines heal quickly and can last for weeks, if not months. To speed up healing, your doctor might recommend conservative treatments. Below are some treatment options.
Medications
There are over-the–counter remedies for mild to moderate pain that can help with pain relief. For severe pain, your physician may prescribe stronger painkillers. You may consider short-term treatments with muscle relaxants if you suffer from severe muscle spasms.
Cortisone injections
Corticosteroid injections could be used to reduce pain and inflammation around nerve roots. Cortisone shots do not provide long-term pain relief. They also allow the body to heal itself.
Physical therapy
Your doctor may recommend physical therapists to restore mobility and strengthen the spine and surrounding muscles. The therapist can work closely with your to strengthen your core muscles.
Lifestyle changes
A doctor might suggest you modify your lifestyle to include regular exercise, weight loss, and regular exercise. Regular exercise is a great way to increase strength, flexibility. mobility and mobile functionality for your joints. Weight loss can ease stress on your spine, joints, muscles.
When is disc extrusion recommended surgery?
If your disc condition doesn’t improve after your first treatment or if you have any severe symptoms, such as persistent pain or intractable movement, weakness or problems with the bowel and bladder, or if your neck or back isn’t improving, then surgery may be required. If there is evidence of nerve damage or disc protrusions, then surgery may be recommended. If medications fail to relieve pain in your spine, a spine specialist may be able help you live the life you want.